Sheath blight and rice blast, bacterial blight are the three major diseases of rice. Now the early rice in the south has been basically closed, and the sheath blight is about to enter a high-risk period of onset. Today, we will talk about the common diseases on this rice.
1, the symptoms of sheath blight
Sheath blight begins to occur at the end of rice tillering, and occurs after the closure of the line to the break period, and very few will occur on the late rice seedlings. Dark green spots appeared on the near-surface leaf sheath, and gradually expanded into cloud-shaped lesions, which seemed to be boiled. The germs spread horizontally first, and then gradually develop upwards and upwards, which will spread the infestation of leaves and stems. When the booting stage is seriously damaged, the ear can not be extracted, and the ear becomes brown and necrotic. If the flag leaves are seriously damaged, there will be an increase in empty mites and a significant reduction in yield.
2. The occurrence law of sheath blight
The bacterium is overwintering in the soil with sclerotia. It can also be overwintered on the residue and weeds of rice plants. When ploughing in the spring of the next year, sclerotia, rice piles, weeds and other sundries float on the surface of the water. The sclerotia adheres to the leaf sheath near the surface of the rice plant. When the field is hot and humid (mostly at the end of the tillering-booting stage), the mycelium produces hyphae invading the leaf sheath, and the growing aerial hyphae infects the adjacent rice plant. First, the rice leaf sheath spreads and spreads in the horizontal direction, and then gradually develops vertically upward. The leaf sheath is infested first, and then the leaves, stems and ears are gradually invaded. After the rice is sealed, the field is shaded and the temperature is getting higher, especially at jointing-booting stage. Due to the development of young ears, the rice plants are compact and the base is compact. The ventilation and light transmission are poor, and the rice plants are rich in nutrients, which is beneficial to the rapid propagation of the pathogens. The cotton hyphae (spider-like) white hyphae are often seen in the field, and the newly formed brown and black sclerotia on the rice plants.
3. Factors affecting the occurrence of sheath blight
Number of bacteria: The field sclerotia is the main source of the initial infection of sheath blight, followed by the mycelium of the epiphyte in the rice plant. In the last year, the field was seriously ill, leaving a large number of sclerotia. favorable.
Climatic conditions: The sheath blight occurs in a high-temperature and high-humidity environment. In the early stage of early rice tillering, the temperature is not high, and the ventilation and light transmission in the field is good, which is unfavorable. After the rice is sealed, the field is shaded, the base is poorly ventilated and light, and the humidity is high. At this time, the temperature is getting higher, which is beneficial to the nucleus germinating mycelium, infecting the leaf sheath, and spreading horizontally and vertically, and the booting stage is particularly prosperous.
Cultivation management: long-term deep-water irrigation, untimely drying of the field, partial application of nitrogen fertilizer, late application of nitrogen fertilizer, green glutinous green, and insufficient potassium fertilizer all contribute to the development of sheath blight, and the incidence is often earlier and the incidence is heavier.
Variety resistance: high-quality rice with compact plant shape, thin stems and scent (such as Zaoxiang No.1 and Meixiangzhan No.2), not resistant to fertilizer (sensitive to fertilizer and water, a little bit of fertilizer is very good) It is susceptible, but the varieties with loose plant shape, thick stems and fertilizer resistance are slightly better.
4, prevention and control measures of sheath blight
Strengthen the management of fertilizer and water: increase the application of phosphorus and potassium fertilizer, promote the use of silicon fertilizer, and timely and appropriate application of nitrogen fertilizer; timely drying the field, promote the development of root system, good activity and enhance disease resistance.
Reasonable drug control: 20 to 25 days after planting, combined with the treatment of aphids and spider mites, the use of 10% hexaconazole 40 ~ 60 grams + 10 grams of silicone in advance prevention, can delay the onset time after the closure of the field, and The degree of disease should be light, reducing the base and reducing stress for later prevention and control. Organic rice cultivation can also be controlled by Trichoderma and Shield Mold.
Sealed line - jointing stage, combined with leaf-rolling insects, planthoppers, and spider mites to prevent and control drugs, 60 grams of 10% hexaconazole alcohol (or 24% thiofuramide 20-30 ml, 30% difenoconazole) Cyclic azole 20 ~ 25 ml, 12.5% ​​flucyclazole 40 ~ 50 ml) + silicone 10 ~ 15 g, such as the field when the disease is heavier, can be mixed with 8% Jinggangmycin A water 250 ~ 300 ml .
5 to 7 days before the break, combined with breaking the mouth medicine and then using the above formula to prevent and control once.
The shallow water layer is reserved in the field during the application to facilitate the systemic conduction of the medicament.
More pesticide knowledge , please pay attention to China Pesticide Network
About this Stainless steel TPR wheel, we use high quality 304 stainless steel. It has great anti-rust effect. And Single wheel is TPR material. It is Single bearing.
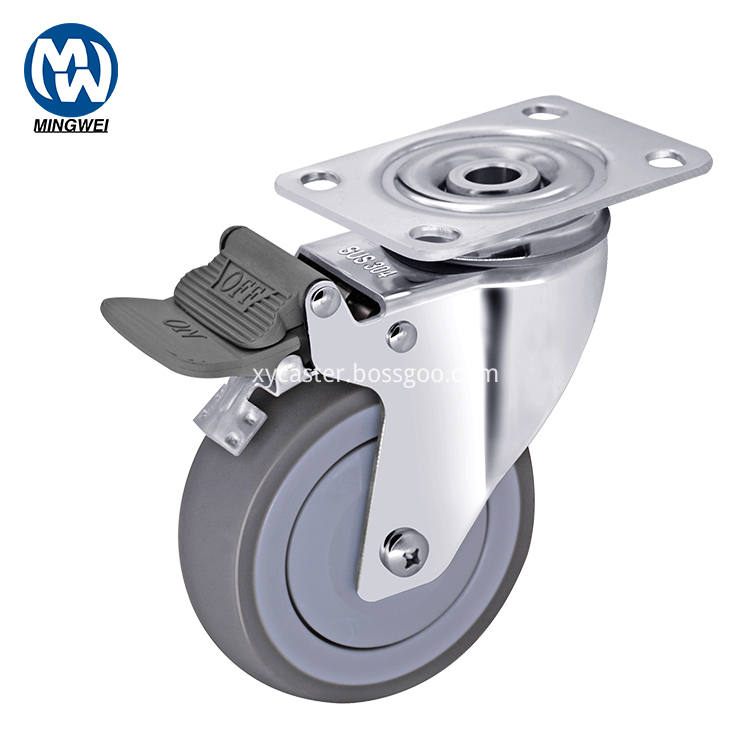
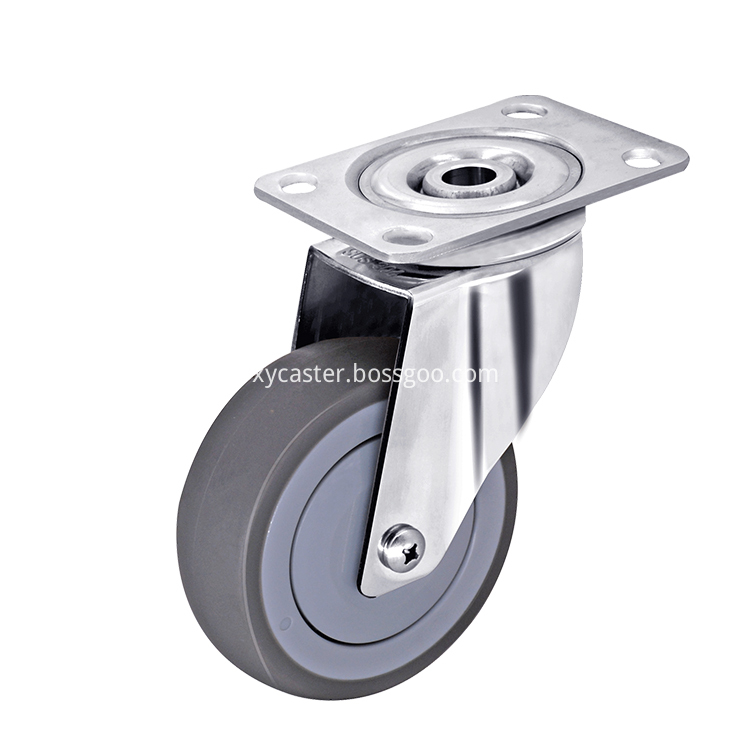
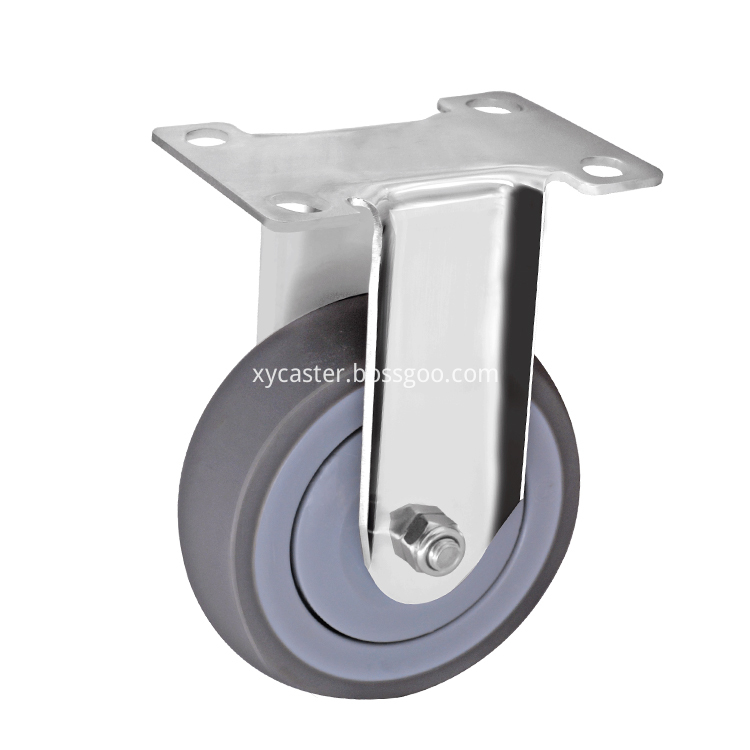
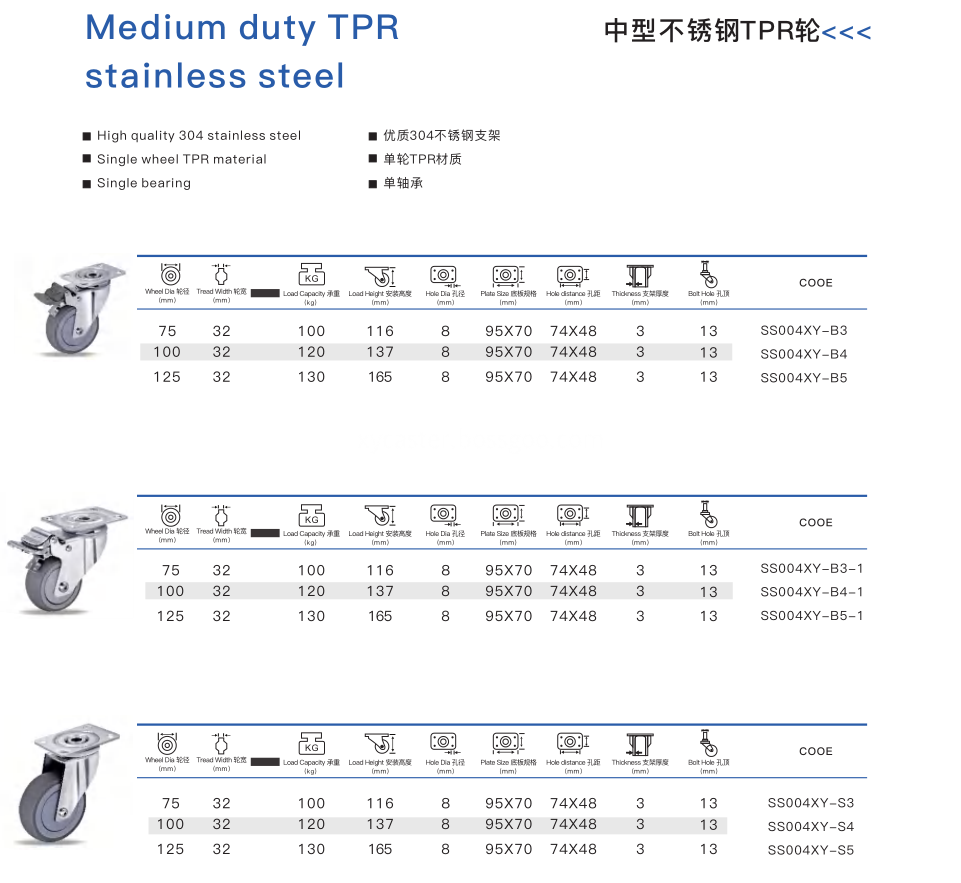



Stainless Steel Casting,Stainless Steel Caster Wheels,Stainless steel TPR wheel, TPR caster Wheel
Yangjiang Xingyang Industry & Trade Co.,Ltd. , https://www.xycaster.com