Recently, the team led by Li Chilin, a researcher at the Shanghai Institute of Ceramics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, has made new progress in the study of fluorine-based energy storage materials. They first proposed that the cubic perovskite phase can be used for high-rate sodium storage electrodes without significantly altering ligand links. In the case of the method, the open frame of the known structure prototype can be realized only by manipulating the channel filling, and the positive electrode material of the sodium ion battery having excellent electrochemical performance is obtained. The relevant paper is published online in "Adv. Funct" (Adv. Funct). Mater. 2017, 1701130).
Due to its abundant resources, low price and potential rate performance advantages, sodium-ion batteries have a wide application prospect in the static energy storage market. The inhibition of the phase transition of the electrode material during the cycle and the expansion of the solid solution reaction zone facilitate the realization of high rate and long cycle. However, many known mineral phases and their derivatives are unable to achieve smooth sodium ion diffusion in the crystal lattice due to the generation of new phase interfaces in the electrochemical process. Large-size sodium ions have to pass through the higher energy barrier solid phase. The interface, so even at low magnification, can also lead to attenuation of capacity and cycle life.
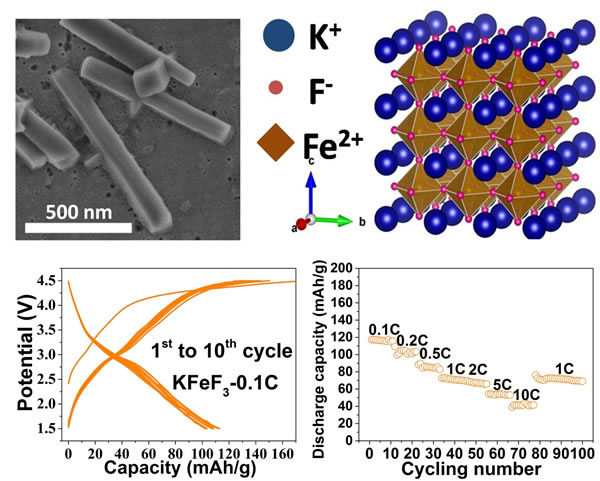
Changing the ligand linking method is conducive to constructing a spacious migration path with more dimensions and mitigating the generation of multiphase interfaces. This strategy has been successfully applied to iron-based fluoride cathode materials. Ferric fluoride has potential energy density advantages. However, commercial ReO3 phases have narrow ion channels and poor intrinsic conductivity. Even if a large amount of carbon is added and the particle size is reduced, the sodium storage performance cannot be alleviated. Attenuation. By adjusting the arrangement of Fe-F octahedrons and introducing water molecules as channel fillers, some open-frame mineral phases such as the pyrochlore phase FeF3•0.5H2O (J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 11425- 11428), hexagonal tungsten bronze phase FeF3 • 0.33H2O (Chem. Mater. 2013, 25, 962-969) and tetragonal tungsten bronze phase K0.6FeF3 (J. Mater. Chem. A, 2016, 4, 7382-7389), Discovered and applied to cathode materials for sodium-ion batteries, their sodium-storage electrochemistry is activated even in the presence of small amounts of carbon-doped carbon and large particles. However, their rate performance has yet to be improved, so new structural prototypes and minerals are explored. Phase is crucial for the development of high-rate fluorine-based cathode materials for sodium-ion batteries.
Cubic perovskite is a research hotspot for solar cells, fuel cells and electrocatalysis in recent years, but it has rarely been attempted as an energy storage electrode due to its dense structure characteristics. In fact, the perovskite phase of the robust framework has intrinsic three-dimensional diffusion channels, but the previously reported Na-filled NaFeF3 channels are narrow, resulting in distortion of the Fe-F octahedral lattice, making channels in certain directions more Narrow, affecting the realization of its high rate of sodium storage. In order to achieve the regularization and opening of the perovskite phase, the team proposed to replace the Na+ as the channel filler with an equal molar number of K+ and synthesize a cubic phase of KFeF3 by the liquid phase method. KFeF3 acts as a positive electrode in the 3V region, achieving a highly symmetrical and isotropic three-dimensional fast ion channel in the crystal structure, exhibiting the electrochemical behavior of a solution reaction (near zero stress) and a high intrinsic diffusion coefficient (7.9–9.8). × 10−11 cm2 s−1), so that the reversible sodium storage capacity can reach 110, 70, and 40 mAh g −1 at 0.1, 2, and 10 C, respectively, which is also the highest reported rate of fluoride sodium storage. performance. At the same time, the team for the first time tested this fluoride as a positive electrode material for potassium ion batteries and has a stable discharge capacity of 60 mAh/g at 0.5 C.
The research has been funded and supported by the Chinese Academy of Sciences 100-person plan, the National Natural Science Foundation, and the national key R&D programs.
The design of the towel rack should consider whether it is convenient or not, but also consider the waterproof problem. Home use towel rack , brass toilet paper holder Bathroom Series, made of high quality brass material,chrome surface corrosion resistance long lasting use for years and years, no worries about rusted and oxidized.
Bathroom Accessories,Towel Rack Stand,Wall Mounted Towel Rack,Outdoor Towel Rack
HESHAN CAIZUN SANITRAYWARE CO.,LTD , https://www.nbcaizunsanitaryware.com