Thermoelectric conversion materials can realize direct conversion between thermal energy and electric energy, and have important applications in aerospace special power/heat flow management, waste heat/cogeneration and portable refrigeration. The thermoelectric properties are characterized by a dimensionless figure of merit (ZT = S2σT/κ). High conversion efficiency requires that the material's power factor S2σ be as high as possible and the thermal conductivity κ be reduced as much as possible. Recently, around several new types of environmentally friendly thermoelectric materials such as SnSe and SnTe, the Optoelectronic Functional Materials and Devices team of the Advanced Manufacturing Institute of the Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, has been closely linked with theory and experiments, and has conducted a series of thermoelectric properties regulation. research work.
In 2014, the new thermoelectric material SnSe reported by Nature magazine had a very low thermal conductivity (0.3W-1K-1) and the highest ZT value (2.6). However, subsequent researchers found that the thermoelectric properties of SnSe materials changed. Larger and less repeatable. Based on this, the team developed a horizontal gas phase method to prepare high-quality SnSe single crystals and carried out relevant measurement work on intrinsic carrier transport, phonon transport, and phase transition. It was found that the intrinsic thermal conductivity of SnSe single crystal at room temperature was 2.0W-1K-1, and it decreased to 0.55W-1K-1 at 773K. This study proposes the variation of the carrier concentration, mobility, effective mass and deformation potential constants of SnSe before and after phase transition with temperature, and describes the SnSe intrinsic carrier transport operation as a single parabolic energy band model. This indicates the idea of ​​SnSe's performance control and reasonably predicts the optimized thermoelectric properties of SnSe. Related research results were published on ACS Energy Lett.
Energy band engineering is an effective method to regulate the electrical properties of thermoelectric materials. In the previous work, the team has optimized the thermoelectric properties of SnTe through two energy band engineering mechanisms: “band degeneracy†and “resonance energy levelâ€. It also clarified the lower concentration of In and the appropriate amount of Mg, Mn, and Cd. The co-doping of Hg and other elements will make the two energy-band regulation mechanisms work synergistically, and the SnTe's thermoelectric performance will be fully enhanced in the larger temperature range. The team prepared samples of In-Hg co-doped SnTe by hot pressing and confirmed that the synergistic action of the two control mechanisms significantly increased the Seebeck coefficient. Further studies have found that after the temperature rises, energy band regulation and resonance energy level will gradually change from synergy to competition. The study further enriched the design connotation of thermoelectric material energy band engineering. The relevant research results were published on J. Materiomics.
Structural design is an effective way to regulate the phonon transport of materials, especially in layered thermoelectric materials. The team inserted a small amount of Na between the MoS2 material layers, achieving a significant reduction in lattice thermal conductivity. It is considered that the decrease of the thermal conductivity of the La intercalation layer in the Na intercalation layer is mainly reflected in two aspects. One is the decrease of the phonon vibration frequency, and the other is the increase of the local phonon frequency branch. The Na-intercalated MoS2 enhances the anharmonic interaction of the low-frequency branch phonons and increases the number of phonon scattering channels, which reduces the phonon lifetime by 1-2 orders of magnitude. This study provides in-depth understanding and feasible ideas for the regulation of thermal conductivity of similar thermoelectric materials. The relevant research results are published on J. Phys. Chem. C.
The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the National Key Research and Development Program, the Zhejiang Outstanding Youth Fund, the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province, and the Ningbo Science and Technology Innovation Team.
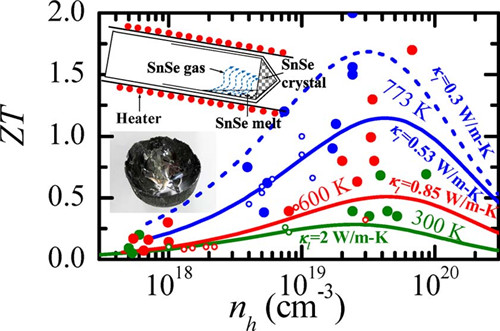
Figure 1. SnSe single crystal preparation and thermoelectric value
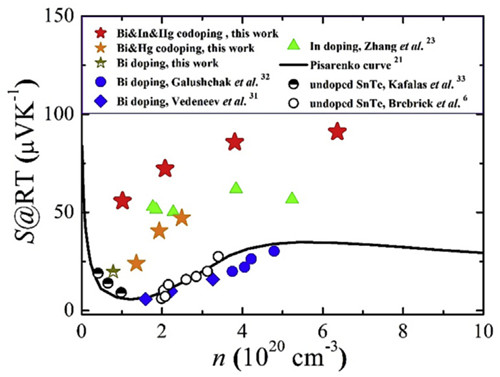
Figure 2. Increased Seebeck coefficient in In&Hg co-doped SnTe
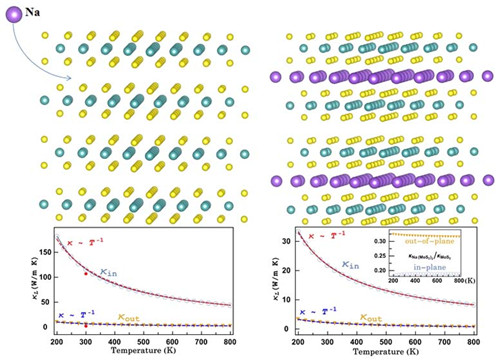
Figure 3. Lattice thermal conductivity of Na intercalated MoS2
125mm Wall Chaser Groove Cutting Machine
The 1700W 125mm Wall chasers are a twin bladed power tool which used to cut groove on brick, stone or concrete walls, perfect for electricians and plumbers, to lay wires or water pipes in the wall.
The 1700W 125mm Wall Groove Cutting Machine Chaser with Cutting Depth 0-28mm, cutting Width 14/19/29mm.
The Concrete Wall Cutting Machines With Spindle lock for easy blade change.
BTW, The Groove Wall Chaser Machine with Laser Function for cutting line straight.
The Wall Chaser work efficiency is much higher than the 5 blades wall chaser, and Less Dust with dust blower.
The 125mm Wall Cutting Machine is comfortable to use, due to anti-slip handle with soft grip cover.
The 1700 Brick Wall Chaser With Guide handle for easy work with little effort.
125Mm Wall Chaser Groove Cutting Mchine,Marble Cutter,Wall Cutter,Wall Chaser Grooving Cutting Machine
Ningbo Brace Power Tools Co., Ltd , https://www.bracepowertools.com