In the gear cold forming (finishing) process, the gear is gradually extruded through the cold forming die, and the internal stress and deformation of the mold are related to the position of the gear. In particular, changes in radial pressure will determine the deformation of the mold. If a suitable mold shape can be designed, the deformation of the mold can be utilized. For example, when the gear is at the entrance and exit of the mold, the force of the mold is relatively small, so the deformation is relatively small. When the gear is in the middle of the mold, the deformation of the mold is relatively large. This feature may be utilized to obtain gear teeth having a drum shape. Literature [6] theoretical analysis and experimental study of drum formation with angled hollow cylindrical parts.
The finite element method is used in the gear cold forming (finishing) process to analyze the deformation of the mold, the deformation of the gear and the rebound. The effect of the forging gear balance, mold shape, size and structure on the final product is considered. Figure 5 is a finite model for analyzing the cold forming process of cylindrical spur gears. The deformation of the punch has little effect on the shape of the gear, so it can be handled as a rigid body in the finite element model. The deformation of the mold cavity directly affects the shape and size of the contour, so the mold is simulated as a deformation body. During the cold treatment, only the tooth surface is plastically deformed, and most of the teeth and the teeth are elastically deformed. The proportion of elastic recovery is large and the elastoplastic material model must be used to predict the final shape of the contour.
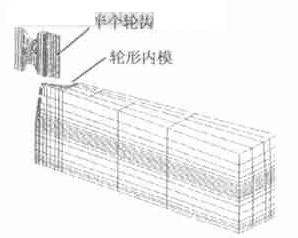
Figure 5 Analysis of the finite element model for cold forming of cylindrical spur gears
Figure 6 shows a mold for cold forming of a cylindrical spur gear. The punch and the core rod are integrated and mounted on the upper slider of the press. There is a small gap between the mandrel and the forged gear hole. It is not used for positioning and is only used to help guide. Because in the forging process, only the accuracy of the teeth is guaranteed and the accuracy of the inner holes cannot be guaranteed. The gear entering the mold cavity is also introduced by the chamfer of the mold.
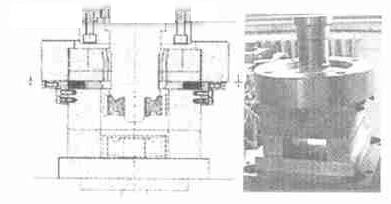
Figure 6 mold for cylindrical cold gear cold forming
If it is to be used for the finishing of the helical gear, the gear will rotate during the squeezing process. A rolling bearing is required between the punch and the press to allow the punch to rotate. In addition, when the helical gear is squeezed, the force on both sides of the gear teeth is asymmetrical and the deformation is different, and the gear can be reversely squeezed once again. In fact, the spur gear can also be treated twice, so that not only the shape of the teeth is good, but also the residual stress state of the surface is better than that of the primary extrusion. After the experiment, the residual compressive stress of 20MPa~50MPa can be obtained by single extrusion, and the residual compressive stress can reach about 100MPa by two treatments [8].
Figure 7 shows the analysis and experimental results of cold forming of a cylindrical spur gear. The profile of the cold extruded gear was measured with a coordinate measuring machine and compared with the results of the finite element prediction. The figure shows the forged gears, the mold, the measured finishing gears, and the contours of the finite element calculations. It can be seen that the theoretical analysis agrees well with the actual measurement. From the analysis, the amount of springback of the contour can be accurately estimated, thereby accurately designing the size and shape of the mold.
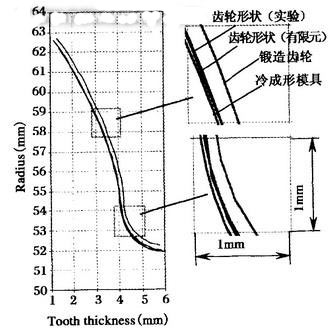
Figure 7 Analysis and experimental results of cold forming of cylindrical spur gears
Another advantage of cold forming is to improve the surface quality of the teeth. Experiments show that the finish is less than Ra = 1μm, which meets the requirements of gear machining [8].
4 Mold manufacturing and gear measurement
The precision of cold forming dies is the key to precision forging technology. The current analytical tools have been developed to a certain level, and a variety of influencing factors can be considered to accurately design the mold. However, there are still many difficulties in manufacturing high-precision molds, especially the gear teeth of the gear precision forging die, which is more difficult to process. Because of the compensation for the elastic recovery of the gear and the elastic deformation of the mold, the gear profile of the mold is no longer a standard involute. Therefore, the data provided to the mold manufacturer is not a standard parameter of the gear, but a data coordinate describing the contour, and usually requires an accuracy of 5 μm or less. For the spur gear mold, wire cutting can be used; but for the helical gear mold, electrolytic machining is required. Wire cutting can approach an accuracy of 5 μm, but this exceeds the accuracy of general electrolytic machining. The grinding process is used to increase the accuracy, and it must be noted that the contour is not a standard gear. In the research topics mentioned in this paper, the manufacture of the mold has been processed and corrected more than twice.
Another key to gear precision forging technology is measurement, including the measurement of molds and gears. Since the teeth of the mold are non-standard gears, it is not possible to use a standard gear for comparison, and there are errors in modulus and other parameters.
The key difficulty in measuring forged gears is their lack of accurate benchmarks. The gear is machined in a conventional manner, and the inner bore serves as a reference for machining and measuring the teeth. However, the accuracy of the gear bore obtained by the forging method is limited and cannot be used as a reference for measurement. In fact, only the teeth have precise characteristics. Therefore, if a forged gear is measured using a standard gear measuring device, it is difficult to avoid positioning errors. It is often the case that the profile can be accurately measured and meets the accuracy requirements, but it is difficult to determine its accuracy level.
5 Results and discussion
After years of experience in gear forging and recent experiments with warm forging and cold treatment, I have the following experience:
1) A universal mold can be used for precision forging of various gears and proved effective in the single-action single crank press;
2) There are mature design methods to ensure the accuracy and consistency of gear hot and warm forging, for example, the contour size has a cold working allowance of 011mm~012mm;
3) The cold forming (finishing) process can be analyzed in detail by modern means, considering various influencing factors, including material, geometry and size, mold deformation and lubrication, etc., to accurately design the mold;
4) The hot and warm forged gears can be cold-formed to achieve ISO6~5 accuracy;
5) There is still a lot of work to be done on mold processing and mold and gear measurement.
Previous page
Modern Soap Dispenser,Soap Dispenser For Hotel,Soap Dispenser Pump For Sink,Kitchen Sink Soap Dispenser
Kaiping Jenor Sanitary Ware Co., Ltd , https://www.kpjenorsanitary.com