Rare earths are effective additives in the metallurgical industry. Rare earth metals have high chemical activity, low potential and special electronic shell structure, which can react with almost all elements. China's rare earth resources are very rich, with complete varieties, good quality, wide distribution and convenient mining. The proven rare earth reserves of 370 million tons, accounting for 80% of the world's reserves, rank first in the world. In recent years,
Rare earths have been widely used in metallurgy, machinery, petrochemical, electronics, atomic energy, medical, agricultural, aerospace and defense industries. The application of rare earths in aluminum and its alloys started late. Foreign countries began in the 1930s, and China began in the 1960s, but it has developed rapidly, especially in the role and application of aluminum and its alloys. The obvious effect. This is mainly concentrated in aluminum-silicon casting alloys, aluminum-magnesium-silicon (zinc)-based deformed aluminum alloys, aluminum alloy wires and piston alloys. Some progress has also been made in the study of the influence of rare earth on aluminum and its alloys and the mechanism of action.
First, the role of rare earth in aluminum and its alloys
Rare earth elements are very active and easily react with gases (such as hydrogen), non-metals (such as sulfur) and metals to form corresponding stable compounds. The atomic radius of the rare earth element is smaller than that of a common metal such as lead, magnesium, etc., and the solid solubility in these metals is extremely low, and hardly forms a solid solution. The addition of rare earth elements to the aluminum alloy can serve as a microalloying property; in addition, it has a strong affinity with gases such as hydrogen and many nonmetals, and can form a compound having a high melting point, so that it has certain hydrogen removal, refining, At the same time, the rare earth element has strong chemical activity, and it can selectively adsorb at the formed grain boundary, hindering the growth of crystal grains, resulting in grain refinement and deterioration.
1. Metamorphism
Modification treatment refers to the process of adding a small amount or a small amount of a modifier to a metal and an alloy to change the crystallization condition of the alloy to improve its structure and properties. The modifier is also known as a grain refiner or an inoculant. Typically, the radius of the rare earth atom is greater than the radius of the aluminum atom. Since the rare earth element is relatively active, it is easily dissolved in the aluminum liquid to easily fill the surface defects of the alloy phase, thereby reducing the surface tension at the interface between the old and the new phase, and increasing the growth rate of the crystal nucleus. At the same time, it can form a surface active film between the crystal grains and the alloy liquid, preventing the generated crystal grains from growing and refining the microstructure of the alloy. Further, as a foreign crystal nucleus, a compound formed of aluminum and a rare earth crystallizes the structure of the alloy due to a large increase in the number of crystal nuclei when crystallizing the metal [1].
Rare earths are mainly metamorphic in aluminum-silicon alloys, which make needles and flake eutectic silicon into spherulites, which reduces the scale of primary silicon.
Different rare earths have different metamorphic abilities, La and Eu have strong metamorphism, while mixed rare earths and Ce have only moderate metamorphism. The metamorphic ability of lanthanides is closely related to its atomic radius. As the atomic radius decreases from 0.187 nm of La to 0.175 nm of Er, the metamorphic ability decreases. In general, the atomic radius is less than 0.18 nm, and the metamorphism is reduced to the extent that it has no practical significance. Literature [12] pointed out that the metamorphic ability of different rare earth elements can be measured by the critical metamorphic cooling rate (Vc). The smaller the Vc is, the more obvious the metamorphic effect is. When V is less than Vc, any concentration of rare earth elements can not cause the alloy to deteriorate. This is one of the main differences between rare earths and other modifiers.
The literature [13] on the Al-Si system shows that the metamorphic treatment process directly affects the metamorphic effect of rare earth. The key to obtain stable metamorphic structure is to reduce the burning loss of rare earth and prevent the segregation of rare earth, so that the rare earth can be quickly and uniformly diffused into the aluminum liquid; in order to obtain stable metamorphic structure, the metamorphic temperature should be increased as much as possible, and the static setting should be strengthened after metamorphism. After refining, the slag is strictly slag, and the halogen element flux is not used for refining and covering as much as possible. Rare earth metamorphism has a certain incubation period and must be kept at a high temperature for a certain period of time, and the rare earth will exert its maximum metamorphism.
2, purification
(1) Degassing effect of rare earth and its influence on pinhole ratio
During the casting process of aluminum and its alloys, a large amount of gas is dissolved in the aluminum liquid, mainly hydrogen (about 85% of the gas in the aluminum liquid), followed by oxygen and nitrogen. The source of hydrogen is mainly water vapor in the charge, oil stains in the aluminum ingots and trim, water, and "aluminum rust" on the surface of the aluminum ingot - Al(OH)3. Hydrogen is the main cause of pinholes in aluminum castings and significantly reduces the strength of aluminum. The literature [4-7] pointed out that the rare earth can be degassed by adding it to aluminum and its alloys. When the rare earth addition amount is less than 0.3%, the hydrogen removal effect of the rare earth is most obvious, and the reduction of the pinhole ratio is also the largest. When the content of the rare earth is more than 0.3%, the hydrogen content decreases when the rare earth content increases. If Y, La single rare earth is used, when the rare earth content exceeds 0.3%, the increase of rare earth content will cause the hydrogen content to start to rise again, and the change of pinhole ratio has the same law, but the variation range is more obvious. The authors believe that the dehydrogenation effect is sequentially Y>La > Re (mixed rare earth); from the addition amount, the single rare earth content is preferably less than 0.3% [10].
According to the literature [8], rare earths with oxygen and nitrogen can form a refractory compound such as Re2O3 and ReN2. In the smelting process, most of them are excluded in the form of slag. Meanwhile, at a temperature of less than 200 ° C, the rare earth can react with fluorine and chlorine to form rare earth fluoride and rare earth chloride, and fluorine and chlorine in aluminum are removed. Therefore, rare earth can be used as a purifying agent in aluminum alloys.
(2) Effect of rare earth removal of impurities and influence on inclusions
The compounds distributed in the matrix and grain boundaries of aluminum and its alloys are various intermetallic compounds, oxides and aluminum oxides. The composition, morphology, distribution and amount of these compounds have a significant effect on the properties of aluminum and its alloys, especially plastic processing properties.
The inclusions in aluminum and its alloys are mainly non-metallic inclusions such as Al2O3, and their presence not only degrades the processability and mechanical properties of the alloy, but also deteriorates the casting properties. In [9], it is pointed out that when 0.2% rare earth is added to pure aluminum (cast state, modified form), the coarse bulk phase of the original intragranular distribution disappears, the spherical rare earth phase is formed, and the strip boundary and the fragment compound are formed at the grain boundary. Significantly reduced, point chain compounds form, forming a homogeneous structure with good plasticity. When 0.2% rare earth was added to the aluminum alloy, it was found that the coarse spheroids originally distributed in the crystal formed a uniform spherical phase on the matrix, and at the same time eliminated brittle fragments and strip compounds at the grain boundary. Finely dotted plastic compounds distributed in a chain and aligned in the direction of deformation. The composition of the constituent phases such as the matrix, the grain boundary compound, the intragranular coarse compound, and the spherical compound in the aluminum and its alloy before and after the addition of the rare earth was measured. It is found that after the addition of the rare earth, the impurities in the aluminum and its alloy, such as iron, are segregated to the spherical phase of the high rare earth, so that the impurity elements at the final solidified grain boundary are greatly reduced, and the grain boundary is purified, so that the crystal The brittle phase of high iron in the boundary is reduced, the grain boundary strength is improved, and the plasticity is improved. The point chain compound distributed at the grain boundary is a low iron, low rare earth composition phase, which is a plastic compound close to the aluminum matrix, especially the rare earth in aluminum. The amount of segregation in the spherical phase of the alloy is larger than that in pure aluminum, so its distribution on the grain boundary of the aluminum alloy is extremely small, so the grain boundary of the aluminum alloy is thinner and more pure than that of pure aluminum.
There are two reasons why rare earths can significantly reduce the number of inclusions [10]:
(1) Rare earth oxides have the characteristics of high melting point and large specific gravity, and their specific gravity is about 2.5 times higher than that of pure aluminum. The greater the specific gravity of the oxide, the more the inclusions sink during the standing process, and the less the amount of inclusions remaining in the aluminum liquid;
(2) After the rare earth is added to the aluminum alloy liquid, the aluminum liquid is stable and does not cause intense boiling like other refining agents. The secondary oxidation is extremely small during the melting process, and thus the amount of the regenerated oxide film (Al2O3) is small. According to the literature [11], the deoxidation ability of rare earth elements is stronger than that of strong deoxidizers such as Al, Mg, Ti, etc., and trace rare earths can desorb [O] to <1×10-4%. The desulfurization capacity of rare earths is also quite strong, and RES or RE2S3 can be formed. The product mainly depends on the activity or solubility of rare earth and sulfur. In rare earth elements, rare earth elements can also react with O and S to form RE2O2S type sulfides. The rare earth element can also be combined with low melting point metal elements such as P, Sn, and As to form compounds such as REP, RESn, and REAs. These rare earth compounds have the characteristics of high melting point and light specific gravity. When their melting point is higher than the metal smelting temperature, a part of the slag can be floated up. Their tiny mass points become the heterogeneous crystal nucleus of the aluminum crystallization process, which serves the purpose of removing impurities from aluminum and its alloys.
Therefore, the rare earth can redistribute the impurities in the aluminum, spheroidize the coarse compound, and purify the grain boundary to improve the plastic working property of the deformed aluminum and its alloy.
3. Alloying
The strengthening effect of rare earth in aluminum alloy mainly includes fine grain strengthening, limited solid solution strengthening and second phase strengthening of rare earth compounds. According to the literature [10], when the amount of rare earth added is different, the rare earth exists mainly in three forms in the aluminum alloy: solid solution in the matrix α(Al); segregation in the phase boundary, grain boundary and dendrite boundary; It is present in the compound or as a compound. When the rare earth content is low (less than 0.1%), the rare earth is mainly distributed in the former two forms. The first form acts as a finite solid solution strengthening, and the second form increases the deformation resistance, promotes the growth of dislocations, and increases the strength. After the rare earth is added, the grain size of the alloy in the as-cast microstructure of the alloy is significantly reduced, and the secondary dendrite spacing is likely to decrease. The intermetallic compounds formed by rare earth elements such as Al, Mg, and Si are spherical and short rod-like. Within the grain boundary or boundary, there is a large amount of dislocation distribution in the structure. When the rare earth content is greater than 0.1%, the latter form of existence begins to dominate. At this time, the rare earth and other elements in the alloy begin to form many new phases containing rare earth elements; at the same time, the shape and size of the second phase are changed, which may cause the second phase to change from a long strip shape to a short rod shape. The size of the particles also becomes finer and is diffusely distributed. Most of the second phase containing rare earth elements are characterized by particle formation, spheroidization and refinement, and this change strengthens the aluminum alloy to some extent.
Second, the application of rare earth in aluminum and its alloys
A variety of rare earth-containing alloy materials have been developed for the unique physical and chemical properties of rare earths. Rare earths are widely used not only in military industry, agriculture, light industry, handicrafts, and transportation, but also as building materials, household appliances, and sporting goods.
Literature [12-13] reports: The application of rare earth in conductive aluminum alloy is an area with wide application, mature technology, high industrial value and good economic benefit. Highly conductive rare earth aluminum alloys generally refer to alloys in which rare earths are added to pure aluminum, aluminum-magnesium-silicon and aluminum-magnesium alloys, and aluminum-zirconium-niobium alloys. It is mainly used to manufacture aluminum wires such as overhead transmission lines, cable wires, sliding wires, wire cores, general wires, special-purpose thin wires and ultra-fine wires. It has developed rapidly, and has been promoted from 3.15 million V to 500,000 V high-voltage lines, ranging from tens of mm2 to several hundred mm2, and has been developed from wire and cable to conductive busbars. They have become a new product in China's conductive aluminum alloy, featuring high strength, large current carrying capacity, long service life, wear resistance and easy processing.
At present, domestic manufacturers of more than 20 provinces and cities produce rare earth aluminum alloy wires, with an annual output of more than 100,000 tons.
1. Rare earth-aluminum intermediate alloy
The single rare earth metal has high chemical property, is easily oxidized and burned during smelting, is inconvenient to store and transport, has high cost, and has too high melting point and high density, and is not easily added to aluminum. Therefore, in most cases, a prefabricated rare earth-aluminum intermediate alloy is used, which not only reduces oxidative burning loss, but also reduces cost, and is convenient to store and transport. When added, the operation is simple and safe, the composition is easy to control, and an alloy with stable composition and reliable quality can be obtained.
2. Application of rare earth in capacitor high purity aluminum
[15-17 ] Report: High-purity aluminum special aluminum foil containing rare earth is an ideal new material for producing low-electrolytic capacitors. Some capacitor factories believe that adding a trace amount of rare earth in high-purity aluminum can significantly increase the corrosion coefficient K of the aluminum foil for the anode of aluminum electrolytic capacitors, while the strength and capacitance are greatly improved. The volume of the fabricated capacitor is significantly reduced, and the material has been used in batches in some capacitors, and has achieved certain effects. However, there are different opinions on the mechanism of action of rare earths, and in-depth research is being carried out.
3. Application of rare earth in aluminum building profiles
Literature [18] reports: In a typical civil building profile 6063 aluminum alloy, the content of rare earth added is preferably 0.17% to 0.25%, and excessive addition will adversely affect various properties. The rare earth has a significant improvement on the mechanical properties and processing properties of the 6063 aluminum alloy. The tensile strength of the deformed profile can be increased by 5% to 10%, the hardness is increased by about 8%, and the elongation is also improved. The bar extrusion preheating temperature can be lowered to increase the extrusion speed. The study also found that after oxidation and coloration of 6063 aluminum profiles with rare earth elements, the film thickness, hardness and gloss of the film were significantly increased, and the corrosion resistance of acid, alkali and salt was improved. In short, after adding an appropriate amount of rare earth to the 6063 aluminum profile, the alloy structure is refined, the color is uniform, beautiful and durable, and is well received by users.
4. Application of rare earth in aluminum alloy window screen
Rare-earth aluminum alloy window screens are superior to the same type of aluminum alloy window screens without rare earths in terms of strength, corrosion resistance, brightness, air permeability, processability and cost, and thus have been widely used. For example, rare earth aluminum alloy window screens produced by Anlu Window Screen Factory and Qijiang Piston Factory have been sold well both at home and abroad.
5. Application of rare earth in daily aluminum products
The addition of trace rare earths to aluminum alloys such as pure aluminum and Al-Mg for daily use aluminum products can significantly improve mechanical properties, deep drawability and corrosion resistance. China's aluminum products factory developed and produced rare earth aluminum alloy pots, pots, lunch boxes, cups and plates and other daily necessities, specific radioactivity is 1.22 × 103Bq / kg, lower than the national standard (1.85 × 104Bq / kg), tensile strength increased by 20% ~ 45 %, corrosion resistance increased by 2.85 times, yield increased by 7% to 20%, aluminum pan can be reduced by 15% to 20% at the same strength, improving material utilization and reducing cost [19]. The Al-Mg-RE alloy sheet developed by Baotou Metallurgical Research Institute has a strength increase of 30% to 40%, an elongation of 30%, and a corrosion resistance of 1 time. It is suitable for the manufacture of various deep-drawn and deep-processed daily necessities. It can be reduced by 15% to 20% and the weight is reduced by 14%. At present, rare earth aluminum alloy daily necessities have been widely used, and the products have increased substantially, selling well in domestic and foreign markets. In addition, some manufacturers have used rare earth aluminum alloys to make washing machine linings, reflections of large spotlights, aluminum bicycle parts and decorative frames, furniture supports, eyeglass frames and other supplies and home appliance parts, and have achieved certain results, prospects. I am optimistic.
6. Application of rare earth in other aspects
Literature [ 20 ] reported that the Ministry of Aerospace 621 obtained the best heat-resistant aluminum alloy material by adding an appropriate amount of rare earth elements to the HZL401 alloy, and is currently using it on the “Sevenâ€. The rare earth aluminum alloy zipper jointly developed by Inner Mongolia Rare Earth Research Institute and Jining Zipper Factory has exceeded its original LF10 alloy. The application of rare earth in aluminum alloy for pen making has also been successful, that is, the modification of domestic industrial pure aluminum by rare earth has replaced the original 99.99% high-purity aluminum. Baotou Rare Earth Research Institute and Jining Aluminum Products Factory have developed and produced rare earth aluminum alloy plate support for printing. It has the advantages of good surface quality, light weight, high strength and hardness, good plasticity, etc., which makes the pad effect good and not easy to be deformed. , can fully meet the requirements of print quality.

Concerned about surprises
Label: Rare Earth Daily Aluminum Products
Previous: Basic knowledge of radioactivity in rare earth production Next: Focus on new developments in agricultural rare earth
Ph orp controllers are widely used in thermal power, chemical fertilizer, metallurgy, environmental protection, pharmaceutical, biochemical, food and tap water industries. With a suitable pH sensor or orp sensor, the pH value or ORP value and temperature in the solution can be continuously monitored. Daruifuno's pH ORP controller has 2 channels of 0/4-20mA current output, supports signal remote transmission and long-term calibration, and also has a two-wire RS485 interface, which can be easily connected to the computer through the MODBUS-RTU protocol for monitoring and recording .
As an online dosing control pH meter, the control function is very important. Our controllers are equipped with 2 relays that can be set by SPST. Customers can set the opening value and closing value to realize the control of the acid-base dosing pump, temperature and cleaning control.
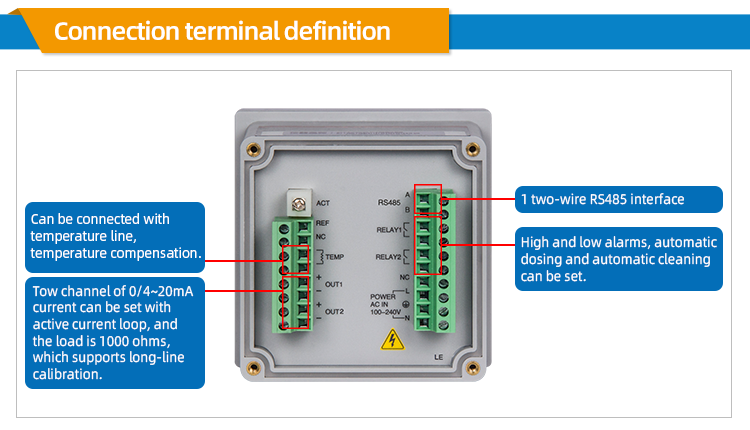
For the convenience of customers, the small-sized pH controller also adds a quick calibration button. The calibration of the pH ORP controller is also very important. It is usually recommended that the electrode needs to be calibrated every 7 days. Our ph meter transmitter supports pH three-point calibration , ORP two-point calibration, and the calibration point can be set by yourself.

In addition, we also have the solution ground ph meter, which can be connected with the SG sensors, used for power plant pure water.
Such a multifunctional pH ORP controller has a very favorable price. We have many models to meet different needs and save costs for customers.
Ph Orp Controller,Solution Ground Ph Meter,Dosing Control Ph Meter,Ph Meter Transmitter
Suzhou Delfino Environmental Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.daruifuno.com